What is economics ?
- amelieriess
- 3. Dez. 2020
- 5 Min. Lesezeit
Today I'm going to introduce you to economics and tell you 10 interesting facts about it.
Let's go!

Let´s start with the needs. First of all, it´s important to know that Human needs are endless. To have a better overview the US psychologist Abraham Maslow has grouped all human needs according to their urgency.
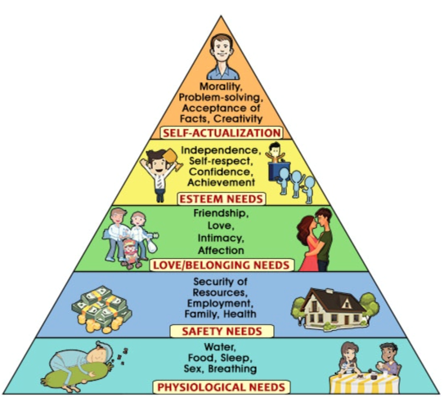
The basic also called physiological needs are Water, Food and Sleep. Next are the Safety needs Health or Family. On the third level is belonging also known as love needs for example Affection or friendship. After this level are the Esteem needs like Self-respect. The last one is self-actualization.
A very important point is sustainability. You need to keep in mind that we only have 1 planet so we must take care of it and live sustainable because our resources are scare.
What are resources? They are factors of production and are used to produce goods. For example, traditional factors are the earth or capital and modern factors are information and innovation. The sake of goods is to feed our needs. So there are two principle, the minimum and the maximum. At the minimum principle you have to reach a given goal with the minimum input possible and at the maximum, principle you have to reach a maximum of output with a given input. Basically economics deals with scarcity and decision making how to share the scarce resources.
Now I want to talk about the Circular flow Model from François Quesnay.

There are two participants in this simple model. On the one side the firms and on the other side the households. Firms supply goods and services to feed consumers ‘needs. The households pay for those in Euro or US Dollars. The households also provide for example labour to firms. Firms pay wages in return. The simple circular flow of a market economy can be expanded by the state, the banks or the rest of the world.
Next one is the division of labour according to Adam Smith the reason for „Wealth of Nations“. About the types. So there are in total 4 types and I’m going to explain them toy you now. The first one is within an enterprise, so different departments like marketing or human resource. The next one is the regional division of labour like wine or fruits from the Wachau valley. The third is the international division of labour. So for example globalization in china. And the last one is the economic sectors within one country. You divide them into primary(agriculture), secondary (industry) and tertiary (retail and services). One advantage is that you have a higher productivity per worker but on the other hand there is potential unemployment.

Another question you ask in economics is how a market work. Th first thing you have to know is that you know that on a market, no matter if it’s a financial or food market, sellers and buyers meet and agree on a price. There is also a market model where you can see the function of prices and quantity. In this model you can find the demand curve(the higher the price, the lower the demand) and the supply curve the higher the price, the higher the supply.
Now to the topic money. Money is everything you can use for payments There are some functions of money like the means of exchange (instead of barter trade), the preserves value, the calculation ( 1€+2€=3€)and the financing(you can ask your bank for a loan) Next there is the value of money. It can change.
1. Inflation & Deflation:
Inflation happens when the level of prices rises so money loses value.
Deflation happens when the level of prices decreases so money gains value.
2. Exchange rates:
Is there a high rate of exchange it´s good for Europeans traveling to US and for imports because you get more US$ per €.
Is there a low rate of exchange it´s good for Americans traveling to Europe and for exports because Americans get more € per US$.

To the goals of economic policy. The economic policy is a sum of all planned measures of the state and other institutions) to stimulate the economy through monetary policy, fiscal policy, labor market and social policy, health and education policy and environmental policy.
In the magic polygon it´s very difficult to realize more goals at the same time because very often you‘ll find conflicting goals.
When you talk about the measurement of econommic activities, GDP you think of Joseph Schumpeter and the business cycles.
What stands for GDP? It’s the gross domestic product, the total yearly income in an economy measurement. The average GDP per head is the sum of all goods & services, reperceive inputs to avoid double counting. Goes the GDP up it means economic growth. This is good for the income or jobs but not for the environment. Goes the BIP down it means recession. This ist good for the enviroment but not for the income and jobs. Alternative for the GDP is for example the human development index (HDI)

The realization of eco market economy in Austria is also important in the Austrian economic. The economist Eucken is the pioneer of this chapter. A little bit information about the social partnership. It´s an important instrument of the Austrian social market economy. Further there is a system of institutionalized cooperation between labour, businesses and government and a cooperation in all important aspects of economic and social policy. They also try to avoid conflicts between the participants of the economic cycle. For the environmental protection there are precisely defined laws
In economics there are 3 types of economic system.
The first one is the free market economy. This system is for example in the UK or the US. In a free market economic system all decisions are taken by private sector organizations and individuals. There is little provision of the legal frame or no role for government or a public sector and therefore little or no taxation or public spending. The economist of this economy is Adam Smith
.
The second one is the planned economy in North Korea. The economist is Karl Marx. In a planned economy all decisions are taken by the state. Decisions on production and distribution of goods and services are done centrally by the state through a planning agency. There no private equity.
The third and last one is the mixed economy. This system is for example in Austria. In a mixed economy a government can intervene in different markets in an attempt to correct the worst market failures. It can provide useful and essential goods and services and also goods and services for people in the greatest need. Further it can employ people in public sector organizations and provide financial support to private sector firms to boost output and employment. In addition, it can outlaw the production of harmful goods and dangerous activities and business practices that restrict competition or mislead consumers. Moreover, it can introduce laws to protect the environment. The economists of this economy are Keynes, Eucken and Rögen.



Kommentare